Thrombocytopenia In Liver Disease
Thrombocytopenia in liver disease. Thrombocytopenia is one of the most common hematological abnormalities and is often the first abnormality seen in patients with chronic liver disease. Additionally thrombocytopenia is a typical problem in patients with some types of both renal and liver disease and may limit therapeutic or diagnostic options. 15 The presence of severe thrombocytopenia can significantly complicate the routine care of cirrhotic patients.
The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia. Thrombocytopenia is a decrease in the platelet count below 150000 in a microliter of blood ie below the lower limit of the reference range which is 150000400000μL. Moderate thrombocytopenia is a frequent finding in cirrhosis of the liver and well tolerated in most instances.
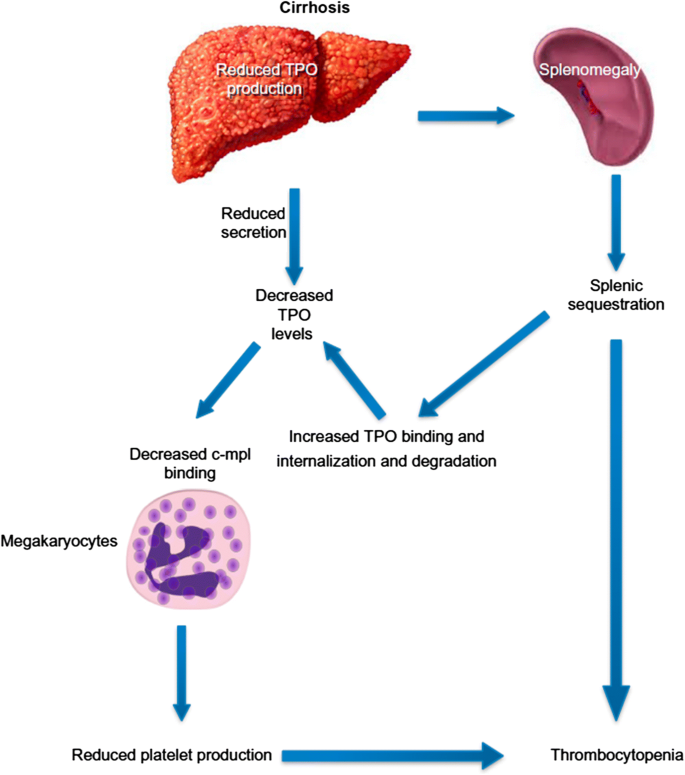
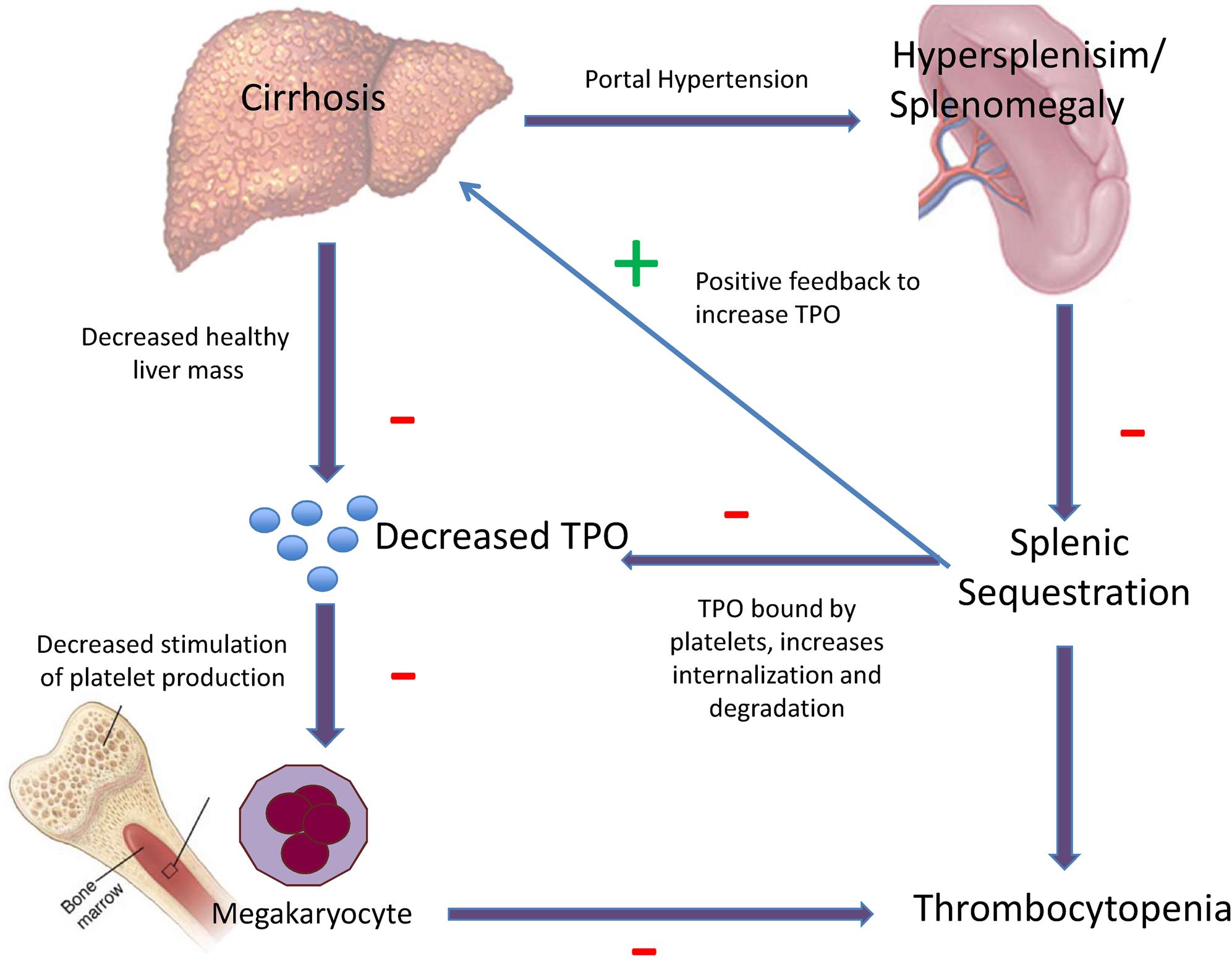
Thrombocytopenia affects approximately 6 of patients without cirrhosis and 70 of patients with cirrhosis. The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia in liver disease has long been associated with the concept of hypersplenism where portal hypertension was thought to cause pooling and sequestratio. Thrombocytopenia is a common haematological disorder in patients with chronic liver disease.
Therefore portal hypertension seems to play some role in thrombocytopenia in liver disease but adequate liver syn-thetic function is essential for the maintenance or. Thrombocytopenia is a common haematological disorder in patients with chronic liver disease. Thrombocytopenia is a relatively common extrahepatic manifestation of hepatitis ceven in the absence of cirrhosisAlso thrombocytopenia has been reported in chronic HBV infection.
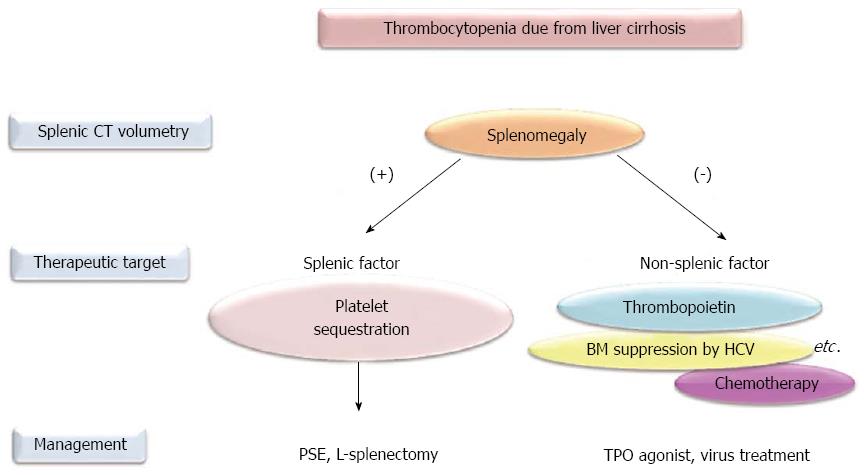
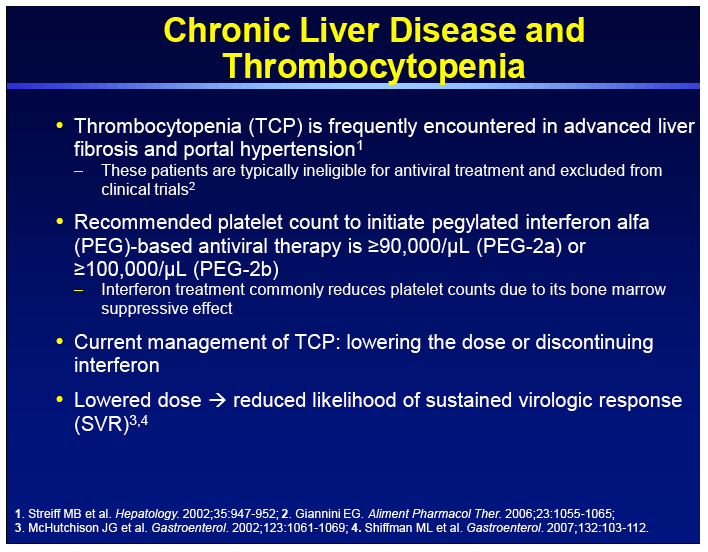
Thrombocytopenia is a common complication in liver disease and can adversely affect the treatment of liver cirrhosis limiting the ability to administer therapy and delaying planned surgicaldiagnostic procedures because of an increased risk of bleeding. Thrombocytopenia is the most common hematological abnormality encountered in patients with chronic liver disease CLD. HLT resolves thrombocytopenia very effectively 37 contrary to the simple relief of portal hyper-tension without restoration of liver synthetic function.
RB Thrombocytopenia defined as a platelet count under 150000µL is probably the most common complication of advanced liver disease or cirrhosis. The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia in liver disease has long been associated with the concept of hypersplenism where portal hypertension was thought to cause pooling and sequestration of all corpuscular elements of the blood predominantly thrombocytes in the enlarged. As a result of the increased risk of bleeding thrombocytopenia may impact upon medical procedures such as surgery or liver biopsy.
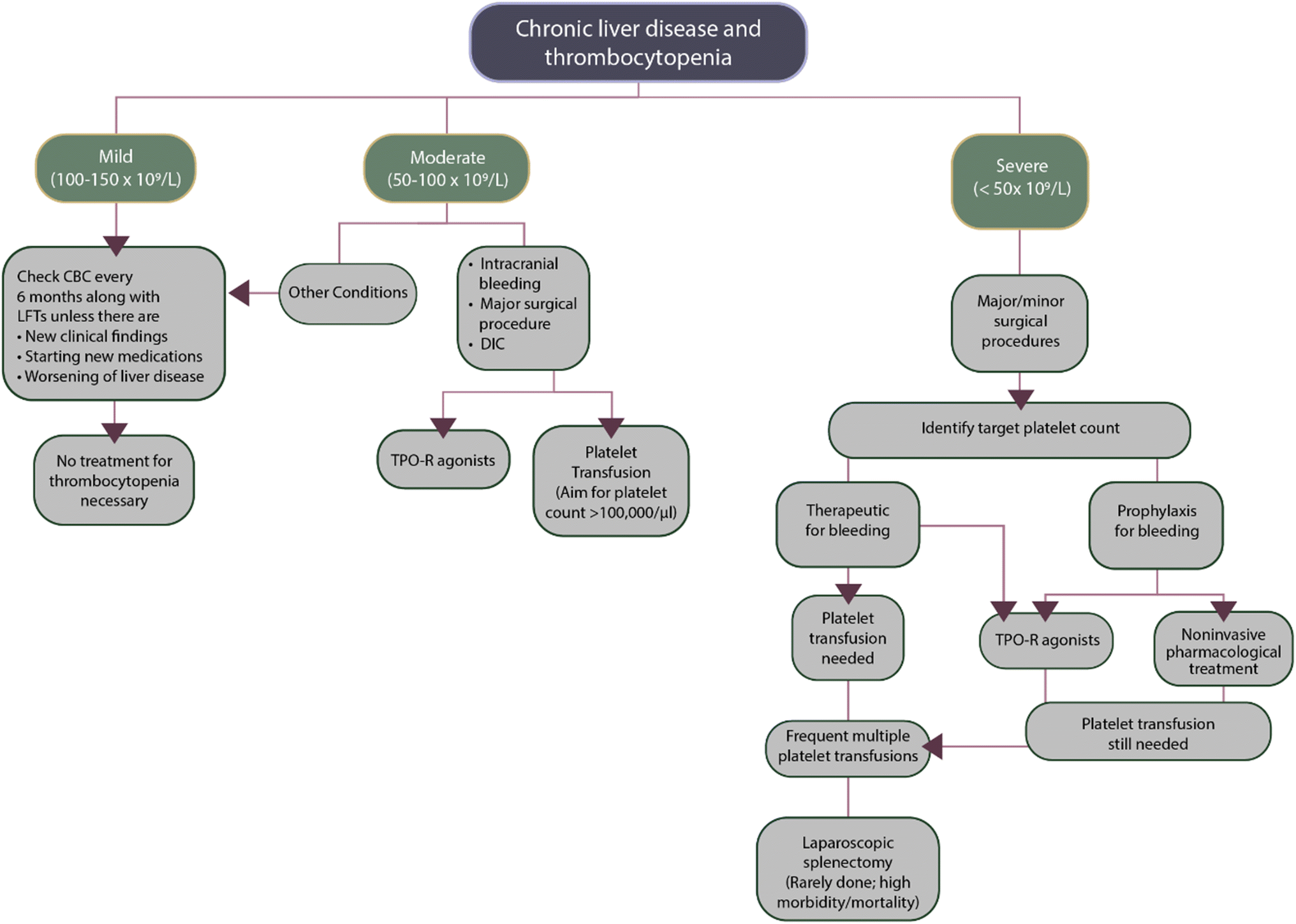
Thrombocytopenia is classified according to platelet count as mild 75000 to. It is multifactorial and severity of liver disease is the most influential factor.
The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia.
The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia. Therefore portal hypertension seems to play some role in thrombocytopenia in liver disease but adequate liver syn-thetic function is essential for the maintenance or. Thrombocytopenia is the most common hematological abnormality encountered in patients with chronic liver disease CLD. Thrombocytopenia in liver disease. Historically thrombocytopenia has been attributed to hypers. This condition tends to occur prior to the clinical manifestations associated with decompensation ie ascites or encephalopathy and is often the first presenting sign of chronic liver disease. Thrombocytopenia is a common complication in liver disease and can adversely affect the treatment of liver cirrhosis limiting the ability to administer therapy and delaying planned surgicaldiagnostic procedures because of an increased risk of bleeding. Standard procedures eg liver biopsies medically-indicated surgeries can pose a substantial risk of bleeding. Thrombocytopenia is a common haematological disorder in patients with chronic liver disease.
Thrombocytopenia is classified according to platelet count as mild 75000 to. The phenomenon of thrombocytopenia related to heavy drinking began to arouse interest in the 1960s and 1970s. Moderate thrombocytopenia is a frequent finding in cirrhosis of the liver and well tolerated in most instances. Thrombocytopenia is a common haematological disorder in patients with chronic liver disease. Bleeding may complicate care of patients with both end-stage renal disease ESRD and cirrhosis. HLT resolves thrombocytopenia very effectively 37 contrary to the simple relief of portal hyper-tension without restoration of liver synthetic function. As a result of the increased risk of bleeding thrombocytopenia may impact upon medical procedures such as surgery or liver biopsy.
































Posting Komentar untuk "Thrombocytopenia In Liver Disease"